Fermentation occurs when there is not enough oxygen present (in anaerobic conditions).
In such conditions, only glycolysis may proceed, but the pyruvate is unable to enter the other components of cellular respiration. The 2 ATPs gained by glycolysis alone is enough to sustain simple life forms, like yeast.
Glycolysis requires the presence of NAD+ which only exists in limited quantities within cells. If this supply runs out, glycolysis can no longer proceed, and the cell will no longer have a source of energy. To overcome this, cells have developed the process of fermentation.
There are 2 types of fermentation: alcoholic fermentation (done by yeast cells) and lactic acid fermentation (done by animal cells)
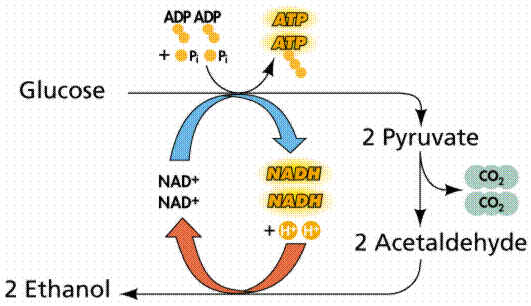
Alcoholic Fermentation:
In alcoholic fermentation, pyruvate is made into ethanol. Ethanol is the final electron acceptor. In the process, NAD+ is changed back to NADH allowing the cycle to continue.
Humans take advantage of alcoholic fermentation to create alcoholic beverages.
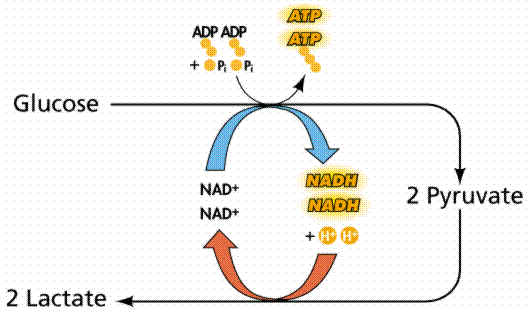
Lactic Acid Fermentation:
In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is made into lactate. Lactate is the final electron acceptor. In the process, NAD+ is changed back to NADH allowing the cycle to continue.
Lactic acid fermentation occurs in human muscles cells during a work out when not enough oxygen is present to meet the demands of the cells. This causes the burn.
No comments:
Post a Comment